Securing life insurance is a crucial step in planning for...
Read More
- Home
- Services
- Premium Rates
- Open Care Senior Plan Rates for 50 to 55 years
- Open Care Senior Plan Rates for 56 to 60 Years
- Open Care senior plan rates for 61 to 65 years
- Open care senior plan rates for 66 to 70 years
- Open care senior plan rates for 71 to 75 years
- Open Care Senior Plan Rates for 76 to 80 Years
- Open Care Senior Plan Rates for 81 to 85 Years
- Open Care Senior Plan Rates for 86 to 90 Years
- Tools
- Blogs
- About US
- Contact Us
Best Life Insurance And Burial Insurance Policies
We are offering you all types of life insurance and final expense insurance policies.
Both term and whole life insurance for the parents and kids.

Life insurance Calculator
How much life insurance is right for you? Find out
Discover financial peace of mind with our Life Insurance Calculator.
Get free quotes for Life insurance and Burial insurance.
Get a No Obligation life Insurance Quote Today
Insure Guardian is committed to providing the best life insurance policies by its association with the best life insurance companies in the USA. Our objective is to keep away our clients from the difficulties that life brings us. We provide them with incredible options and help them in making the right decision.
Discover What Everyone Should Know with Our Free eBook!
Common Myths about Life Insurance
Are you unsure about life insurance? Our latest eBook, “Common Myths about Life Insurance,” uncover the myths and clears up all the misconceptions. Take the First Step Towards a Secure Future.
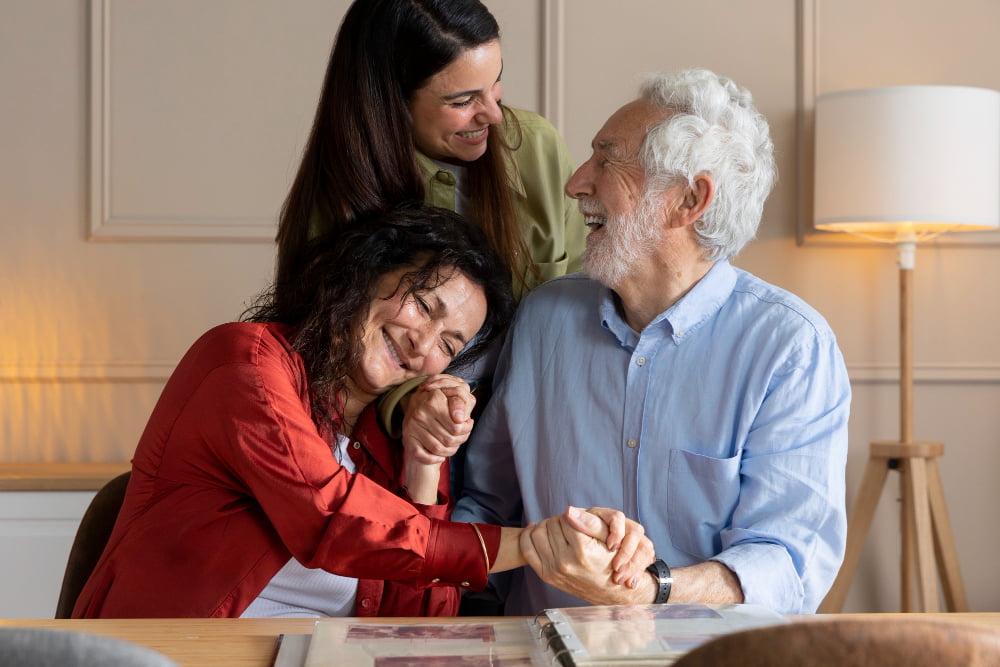
Our New Life Insurance For Parents
In our life insurance policies for parents, we have cared for seniors whose children are looking for life insurance plans for their parents. All types of policies including whole life, term life, universal life, and family plans are available.
Whole Life Insurance With Dividends
Many life insurance policies provide dividends that reflect some of the earnings that the insurance company pays to the policyholders.
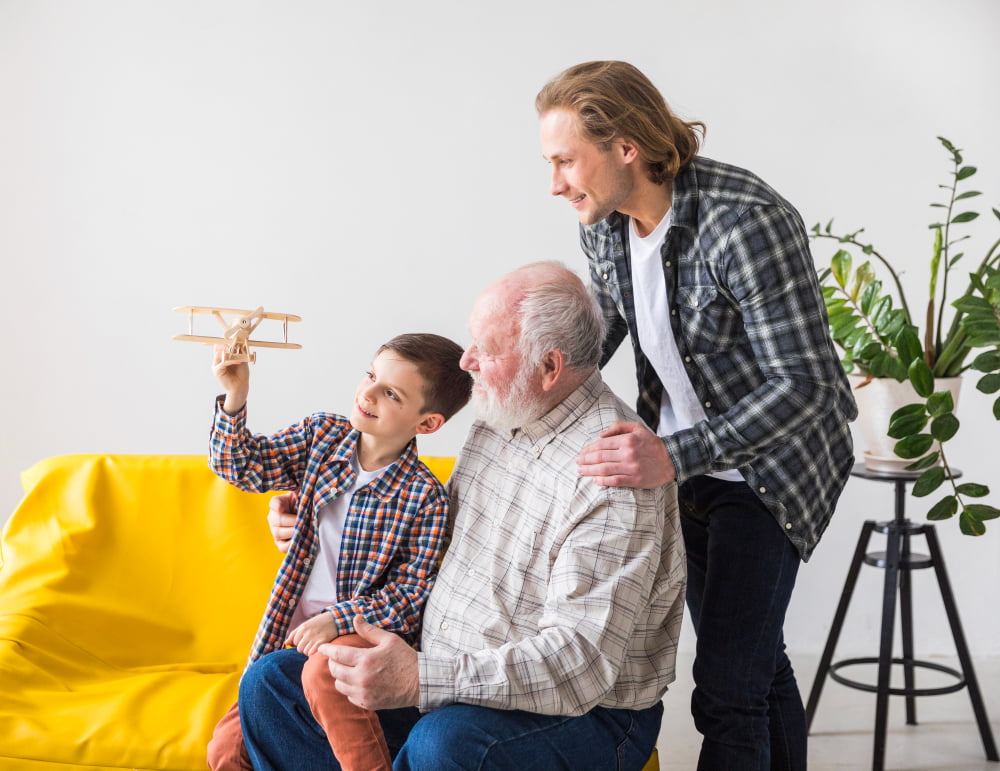
Life Insurance For Parents
How much is the life of a parent worth? Surely, no children in the world want to consider something like this.
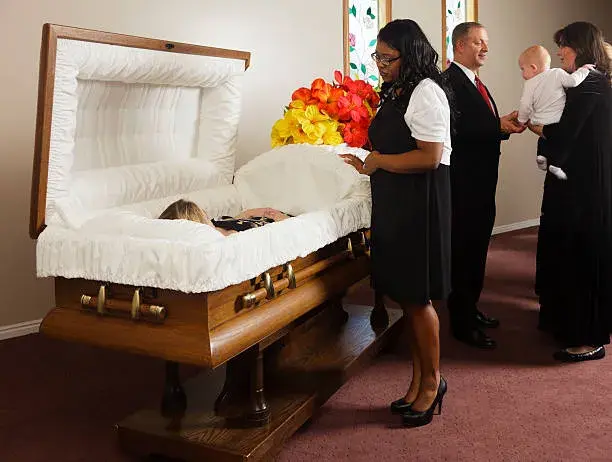
Final Expense For Parents
Death is obvious and you can plan your parent's funeral and burial expenses now with our final expense insurance.

Our unique life insurance & burial insurance policies
With the help of these plans, you will be able to pay the final expenses of your parents, such as medical bills, care in the care center, and funeral expenses, among others.
Demand for life insurance policies is increasing
The graph illustrates the demand for life insurance, final expense insurance, and burial insurance in the USA over time. There’s been a high hike in the demand for all types of life insurance and burial policies after the wave of COVID-19. So don’t wait, get free life insurance and burial insurance quotes now.
Read Our Blogs
We have covered many aspects of the life insurance policies in our blog posts.We are inviting you to read all the blog posts before buying any type of life insurance policy.The blog posts are written in such a way that it covers the questions of the life insurance policy seekers and surely help you to get the best plan for you.
Are Online Insurance Quotes Accurate: Discover Now
The internet has completely changed the way we buy insurance....
Read MoreCan illegal immigrants get life insurance? Coverage Options
Are you wondering can illegal immigrants get life insurance? It’s...
Read MoreNational family assurance corporation scam or Legit?
Is National Family Assurance Corporation the right choice for your...
Read MoreUnder an interest sensitive whole life policy: A closer Look
Are you looking for a way to make your life...
Read MoreIs medical insurance the same as health insurance? Find best
Ever wondered Is medical insurance the same as health insurance?...
Read MoreEmpowering Success Through Our Trusted Partners

























Why Choose Us
Insure Guardian represents a wide variety of amazing life insurance policies. We carefully analyze the requirements of your life insurance policy. Our experts are here to serve you in choosing the best life insurance policies for you and your family.
We are here to help you and your family choose the right life insurance policies.
Partners
All state Insurance
Global life Insurance
GEICO Insurance
Colonial Penn Life Insurance
Fidelity insurance Company
Metlife
M-Life Insurance
Contact Info
Phone: +1(800)695-6528
Email: [email protected]
Copyright 2024 Insure Guardian









